
Properties of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation You can download Communication Systems Sheet by clicking on the download button below
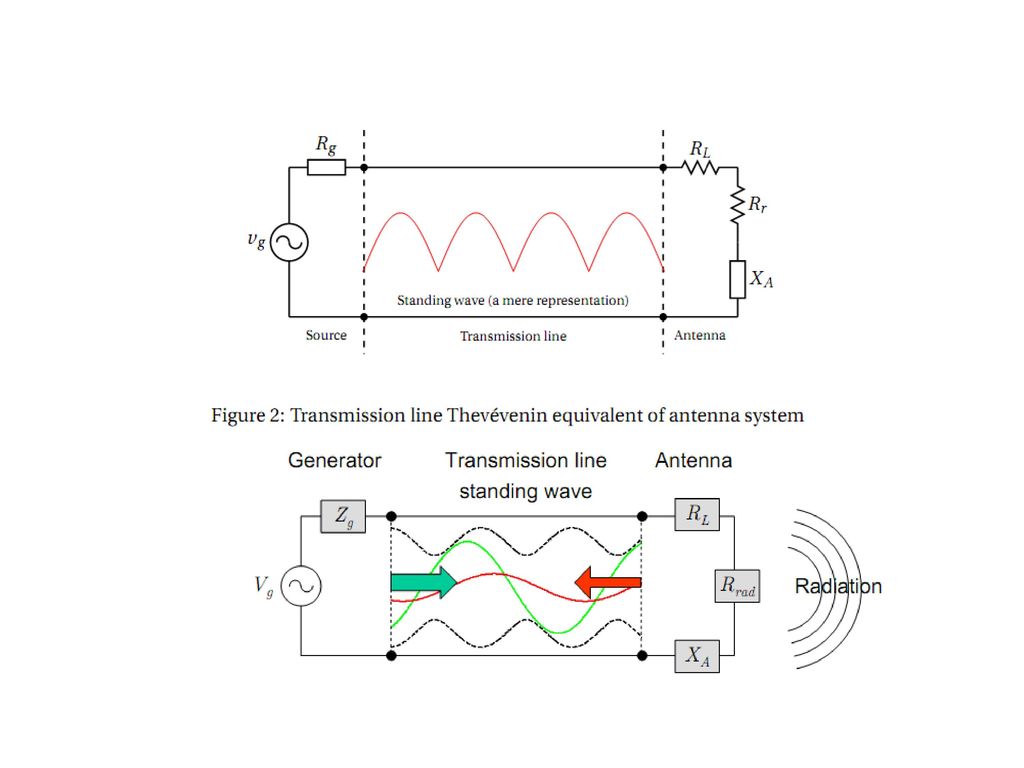
The direction of the propagation of such waves is perpendicular to the direction of the force of either of these fields as seen in the above figure. In simple words, electromagnetic waves are oscillations produced due to crossing over of an electric and a magnetic field. This antennas placed in the height places because of some signals are cannot penetrate throw walls that is LOS, so antennas place a major role in the military, airports, and missile systems.What is Electromagnetic Wave Propagation?Įlectromagnetic Waves also called Electromagnetic Radiations are basically defined as superimposed oscillations of an Electric and a Magnetic Field in space with their direction of propagation perpendicular to both of them.

There are different types of antennas used in the field like bidirectional, helical type, circular type antennas are used. Nowadays antennas are used in many places to send the signal there are two types of antennas one is connected at transmitting side and another is at receiver side.

And it explains you about the ground and sky wave propagation, electromagnetic spectrum, frequency bands. It explains the antenna characteristics, radiation pattern of the antenna, radiation intensity, directivity of the antenna, beam width, efficiency of the antennas and it also explain about the half wave, hertz an, monopole dipoles, and also antenna array types like broad side, end fire arrays, and also V- antenna, inverted v-antenna and derivation of the v antenna, rhombic, long periodic antennas, and helical antennas and different modes of operation of the antenna like transverse electric, transverse magnetic, transverse electromagnetic modes, and also explain you about the antenna ranges, methods for the antenna measurements.
This Antenna and Wave Propagation seminar topic is mainly explain you about the how the antenna is working, types of antennas, antenna arrays, fundamentals of antenna, wave propagation, and which antennas are most reliable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
